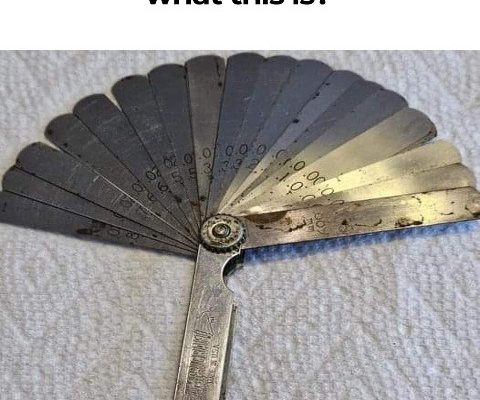
If you’ve ever worked on engines, fine-tuned machinery, or even tackled DIY projects that require precision, you’ve probably come across a feeler gauge. This small but powerful tool has been a staple in mechanical and engineering fields for decades. But what exactly does it do, and why is it so crucial in various industries? Let’s dive into the world of feeler gauges and discover their importance, how they work, and the best ways to use them.
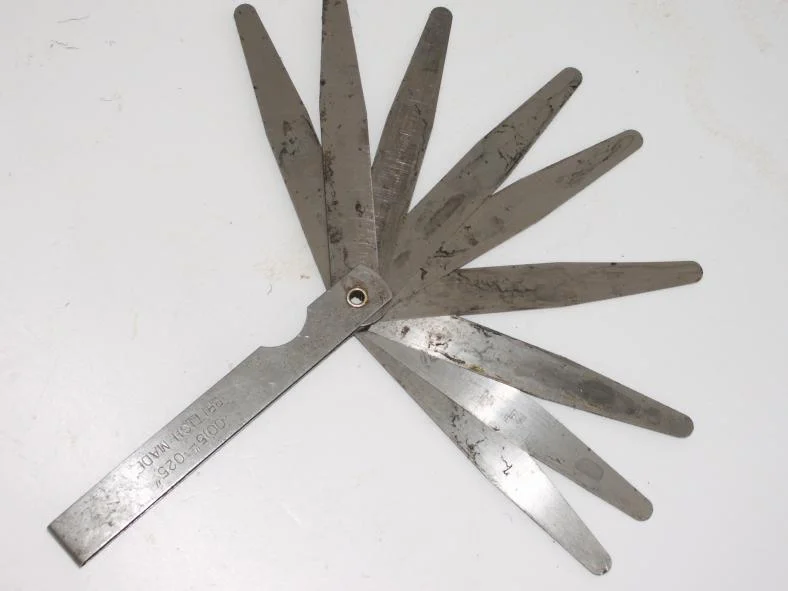

What Is a Feeler Gauge?
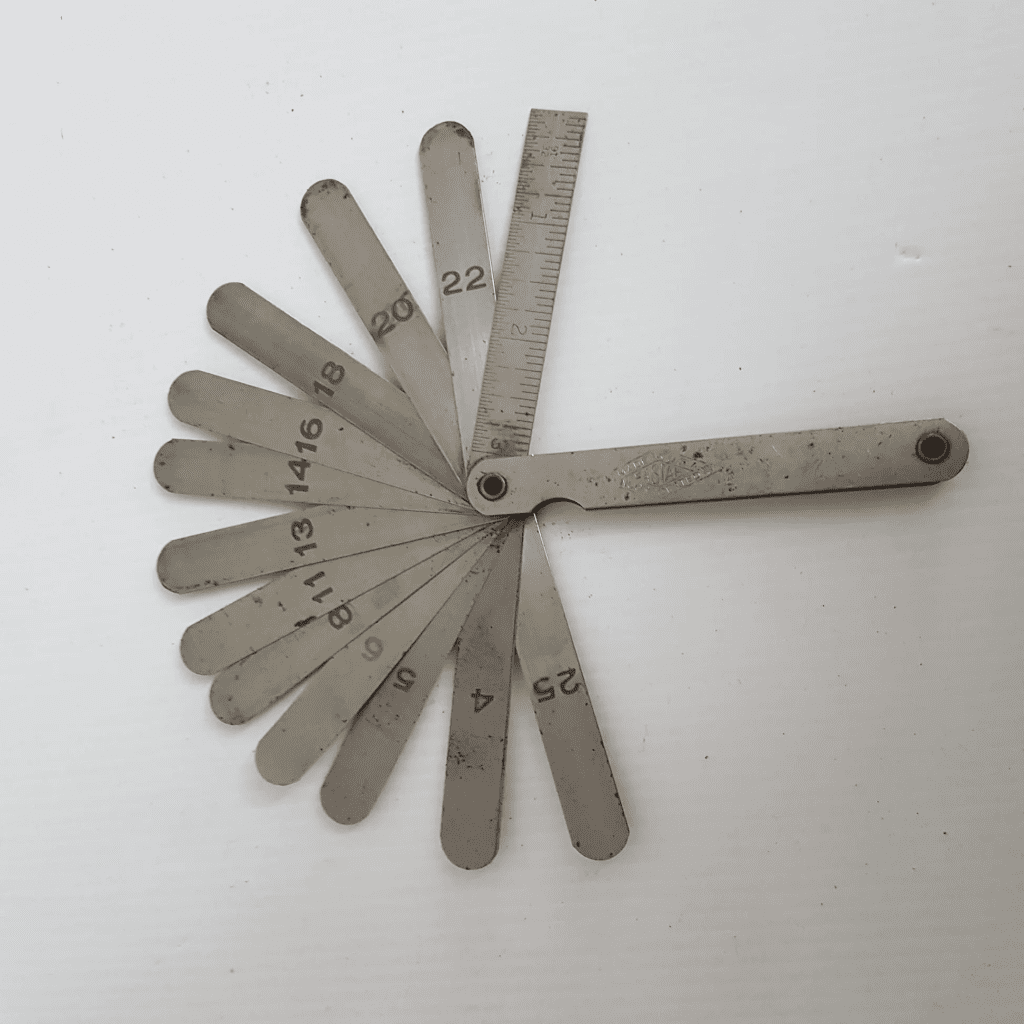
A feeler gauge is a precision measuring tool used to determine and set gaps or clearances between two surfaces. It consists of multiple thin metal blades of varying thicknesses, typically made from stainless steel or hardened tool steel. These blades are marked with their thickness measurements, allowing users to select the exact size needed for their application.
Mechanics, engineers, machinists, and even hobbyists rely on feeler gauges to ensure parts fit together with the right tolerance. Whether it’s setting valve clearances in an engine or checking the gap between spark plugs, this tool ensures precision and accuracy.
Why Are Feeler Gauges Important?
Even the smallest gap or misalignment in machinery can lead to inefficiencies, overheating, or even catastrophic failure. That’s where a feeler gauge becomes invaluable. Here’s why it’s a must-have tool:
- Ensures Accuracy – Helps maintain proper tolerances in mechanical parts.
- Prevents Wear and Tear – Correct clearances prevent excessive friction and damage.
- Improves Performance – Properly adjusted components result in better efficiency and reliability.
- Saves Time and Money – Identifying and correcting gaps early can prevent costly repairs down the line.
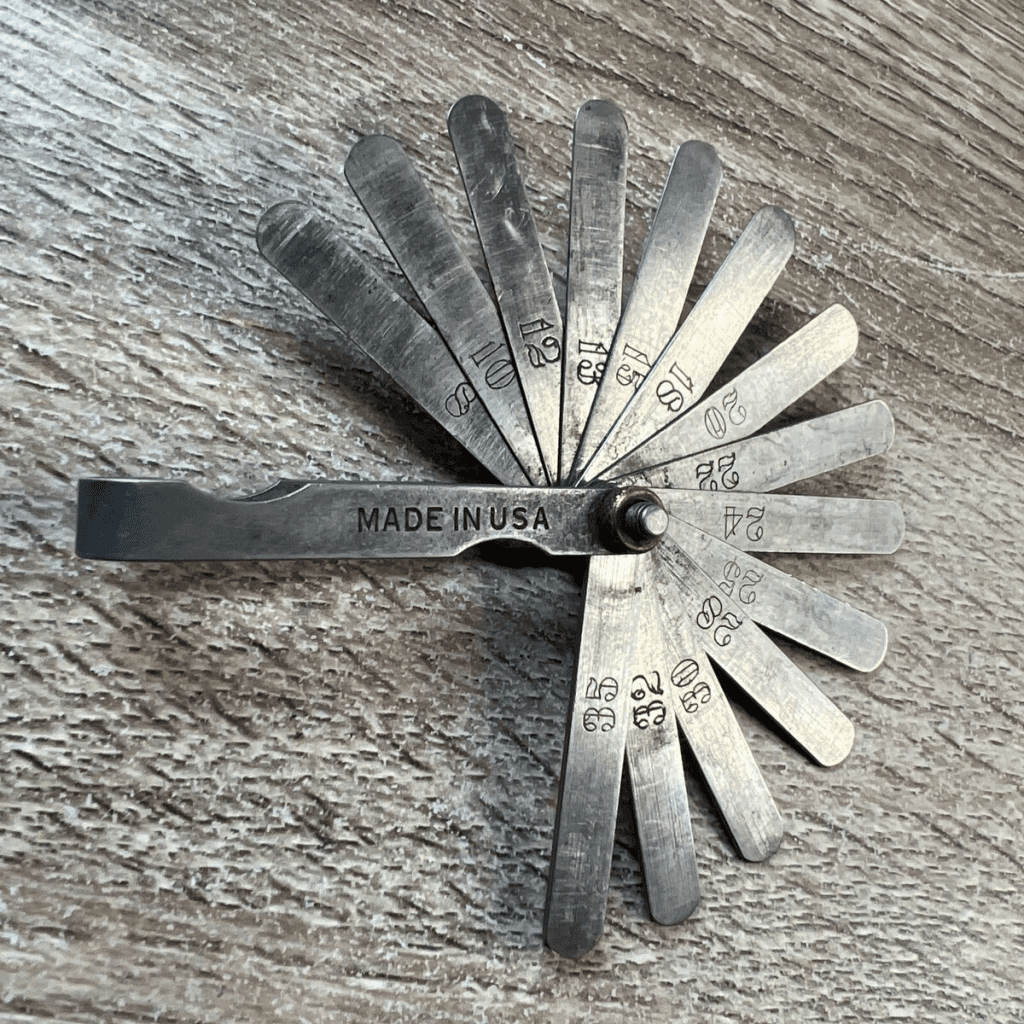

How Does a Feeler Gauge Work?
Using a feeler gauge is straightforward, but precision is key. Here’s how it works:
- Identify the Gap to Measure – Whether you’re working on an engine, a machine part, or an electrical contact, determine the gap or clearance that needs checking.
- Select the Right Blade – Start with a blade that you believe is close to the expected gap. If it slides in too easily, try a thicker one. If it doesn’t fit at all, switch to a thinner one.
- Check for Fit – The correct blade should slide into the gap with slight resistance but without forcing it in.
- Record the Measurement – The number printed on the blade represents the clearance size, helping you adjust or verify specifications.
Some advanced feeler gauges also come with tapered ends, angled blades, or metric/imperial measurements, making them even more versatile.
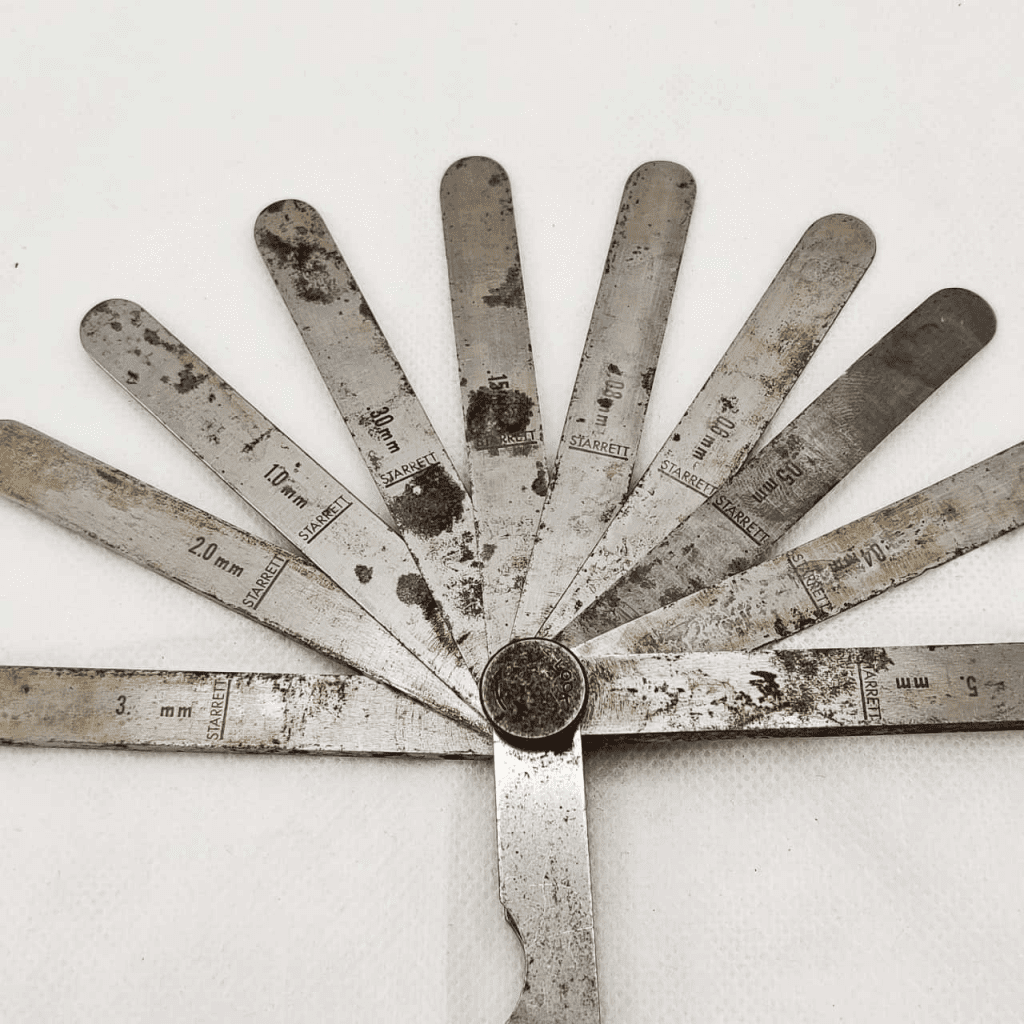

Common Uses of Feeler Gauges
Feeler gauges are used across multiple industries, from automotive repair to precision engineering. Here are some of their most common applications:
1. Automotive Industry
- Valve Clearance Adjustment – Internal combustion engines require precise valve clearances to ensure efficient operation.
- Spark Plug Gap Measurement – Properly spaced spark plugs ensure optimal ignition and engine performance.
- Brake Pad Clearance – Mechanics check the distance between brake pads and rotors to maintain braking efficiency.
2. Machining & Engineering
- Checking Bearing Clearance – Bearings in machinery need precise spacing to prevent overheating and wear.
- Aligning Machine Parts – Ensuring that components fit together properly helps machines run smoothly.
- Checking Tool Setup – Feeler gauges assist in setting up lathes, milling machines, and other precision tools.

3. Industrial & Electrical Applications
- Measuring Gaps in Metalwork – Fabricators use feeler gauges to maintain uniform spacing in welded joints.
- Electrical Contact Measurement – Ensures that electrical contacts have the correct spacing for proper conductivity.
Types of Feeler Gauges
Not all feeler gauges are the same. Depending on the application, different types are available:
- Straight Feeler Gauges – The most common type, with flat, straight blades.
- Tapered Feeler Gauges – Ideal for measuring gaps in confined spaces.
- Angled Feeler Gauges – Designed for hard-to-reach areas, commonly used in engines.
- Offset Feeler Gauges – Feature a bend at the end for use in awkward positions.
- Metric & Imperial Feeler Gauges – Some sets include both measurement systems for flexibility.
How to Maintain Your Feeler Gauge
To ensure longevity and accuracy, proper care is essential. Here’s how to keep your feeler gauge in top condition:
- Clean After Use – Wipe the blades with a clean, dry cloth to remove dirt and debris.
- Prevent Rust – Apply a light coat of oil to prevent corrosion, especially if working in humid environments.
- Store Properly – Keep it in a dry place, preferably in its protective case.
- Avoid Bending Blades – Bent blades can affect measurement accuracy, so handle them with care.
Choosing the Right Feeler Gauge for Your Needs
If you’re in the market for a feeler gauge, consider these factors:
- Material – Stainless steel offers durability and corrosion resistance.
- Range of Blades – A good set should have a wide variety of thicknesses.
- Measurement Units – Some users prefer metric, while others work with imperial measurements.
- Blade Length & Flexibility – Longer blades help reach difficult areas, while flexible ones work well for curved surfaces.
Final Thoughts
A feeler gauge might not be the flashiest tool in your toolbox, but it’s one of the most important for precision work. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic, an engineer, or a DIY enthusiast, this simple yet effective tool ensures that machinery runs smoothly and efficiently.
By understanding how to use and maintain a feeler gauge properly, you can prevent costly mistakes and keep your equipment in peak condition. So, the next time you need to check a gap or clearance, reach for this essential tool—you’ll be glad you did!